LittleDabbie
Supporter
- 11,813
- 438
What is a Stroke?
Strokes, which are injuries to the brain caused by blockage of its blood supply, are the leading cause of severe and long-term disability in the United States. Strokes happen very frequently (approximately once every 40 seconds). Each year, approximately 795,000 people in the U.S. have a stroke, and death is caused in approximately 140,000 cases. Strokes most often occur in those with high blood pressure, and while strokes most often happen in the elderly, approximately 1/4 occur in those younger than 65.
Since blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the brain, stopping or losing blood flow can lead to brain cell injury and death, which may result in a myriad of symptoms including difficulties with or loss of speech, memory, movement, writing, changes in personality, etc. Types of strokes include ischemic (caused by a blockage), hemorrhagic (vessels carrying oxygenated blood to the brain rupture and bleed), and transient ischemic attacks (temporary blockage, “mini-strokes”). The larger the area of the brain impacted and the longer the blood supply remains blocked/reduced, the more likely it is that severe brain damage will occur.
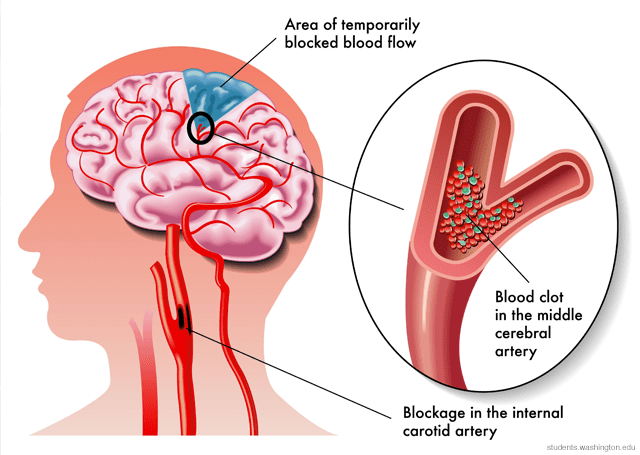
What are the Symptoms of a Ischemic Stroke?
It is important to recognize the warning signs of a stroke so that the patient can be taken to the hospital immediately. These signs include the following (list taken verbatim from WebMD):
Medical Marijuana for Ischemic Stroke Treatment
A recent meta-analysis of 144 animal studies including 1,473 subjects (rats, mice, and primates), published in the Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism in December 2014, found that in those who had suffered an ischemic stroke (temporary or permanent), the amount of the brain injured as a result was reduced in those subjects that had used cannabinoid therapies as opposed to those that had not.
The therapies included endocannabinoids (cannabinoids found within the body inherently), phytocannabinoids [those found in the cannabis plant, including cannabidiol (CBD, a non-psychoactive cannabinoid) and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC, the psychoactive cannabinoid)] and synthetic cannabinoids acting at CB1/CB2 receptors.
While survival was not increased by the use of cannabinoid therapies, scores on measures assessing neurological function were improved after use of all cannabinoid therapies when separated by class (i.e. endocannabinois, phytocannabinoids, synthetic cannabinoids). Individually, the largest impact was seen with HU-210, a synthetic CB1/CB2 agonist (receptor stimulator) that is much more potent and longer-lasting than THC. The most significant effects on brain volume preservation were seen with use of agents within 2 to 6 hours post-stroke, with variation depending on the class of agent used. In many cases a dose-response pattern was recognized (the more agent used, the larger the volume of preserved brain matter).
However, certain individual agents showed no impact in reducing volume of damaged brain matter, or they only reduced the amount of damage at high doses (e.g. SR141716, a synthetic cannabinoid that prevents stimulation of the CB1 receptor). In one case, there was actually more damage caused by an agent (SR144528, a synthetic cannabinoid that prevents stimulation of the CB2 receptor).
Conclusion
While the authors recognize that the meta-analysis is imperfect and carries certain important limitations, it adds to a growing body of evidence which suggests that modulation of the endocannabinoid system may protect the brain from damage.
With further research and as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, standardized use of cannabinoid agents derived from medical marijuana may one day prove useful in reducing brain damage caused by stroke, and therefore has the potential to improve long-term quality of life (and potentially longevity) for hundreds of thousands of people each year.
For information on how you can advocate to reclassify cannabis in order to increase research, expectations, and safety in considering whole-plant medical cannabis use, click here.
http://www.medicaljane.com/2014/12/31/marijuana-may-reduce-brain-damage-caused-by-strokes/
Strokes, which are injuries to the brain caused by blockage of its blood supply, are the leading cause of severe and long-term disability in the United States. Strokes happen very frequently (approximately once every 40 seconds). Each year, approximately 795,000 people in the U.S. have a stroke, and death is caused in approximately 140,000 cases. Strokes most often occur in those with high blood pressure, and while strokes most often happen in the elderly, approximately 1/4 occur in those younger than 65.
Since blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the brain, stopping or losing blood flow can lead to brain cell injury and death, which may result in a myriad of symptoms including difficulties with or loss of speech, memory, movement, writing, changes in personality, etc. Types of strokes include ischemic (caused by a blockage), hemorrhagic (vessels carrying oxygenated blood to the brain rupture and bleed), and transient ischemic attacks (temporary blockage, “mini-strokes”). The larger the area of the brain impacted and the longer the blood supply remains blocked/reduced, the more likely it is that severe brain damage will occur.

What are the Symptoms of a Ischemic Stroke?
It is important to recognize the warning signs of a stroke so that the patient can be taken to the hospital immediately. These signs include the following (list taken verbatim from WebMD):
- Numbness or weakness in your face, arm, or leg, especially on one side
- Confusion or trouble understanding other people
- Trouble speaking
- Trouble seeing with one or both eyes
- Trouble walking or staying balanced or coordinated
- Dizziness
- Severe headache that comes on for no known reason
Medical Marijuana for Ischemic Stroke Treatment
A recent meta-analysis of 144 animal studies including 1,473 subjects (rats, mice, and primates), published in the Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism in December 2014, found that in those who had suffered an ischemic stroke (temporary or permanent), the amount of the brain injured as a result was reduced in those subjects that had used cannabinoid therapies as opposed to those that had not.
The therapies included endocannabinoids (cannabinoids found within the body inherently), phytocannabinoids [those found in the cannabis plant, including cannabidiol (CBD, a non-psychoactive cannabinoid) and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC, the psychoactive cannabinoid)] and synthetic cannabinoids acting at CB1/CB2 receptors.
While survival was not increased by the use of cannabinoid therapies, scores on measures assessing neurological function were improved after use of all cannabinoid therapies when separated by class (i.e. endocannabinois, phytocannabinoids, synthetic cannabinoids). Individually, the largest impact was seen with HU-210, a synthetic CB1/CB2 agonist (receptor stimulator) that is much more potent and longer-lasting than THC. The most significant effects on brain volume preservation were seen with use of agents within 2 to 6 hours post-stroke, with variation depending on the class of agent used. In many cases a dose-response pattern was recognized (the more agent used, the larger the volume of preserved brain matter).
However, certain individual agents showed no impact in reducing volume of damaged brain matter, or they only reduced the amount of damage at high doses (e.g. SR141716, a synthetic cannabinoid that prevents stimulation of the CB1 receptor). In one case, there was actually more damage caused by an agent (SR144528, a synthetic cannabinoid that prevents stimulation of the CB2 receptor).
Conclusion
While the authors recognize that the meta-analysis is imperfect and carries certain important limitations, it adds to a growing body of evidence which suggests that modulation of the endocannabinoid system may protect the brain from damage.
With further research and as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, standardized use of cannabinoid agents derived from medical marijuana may one day prove useful in reducing brain damage caused by stroke, and therefore has the potential to improve long-term quality of life (and potentially longevity) for hundreds of thousands of people each year.
For information on how you can advocate to reclassify cannabis in order to increase research, expectations, and safety in considering whole-plant medical cannabis use, click here.
http://www.medicaljane.com/2014/12/31/marijuana-may-reduce-brain-damage-caused-by-strokes/




